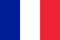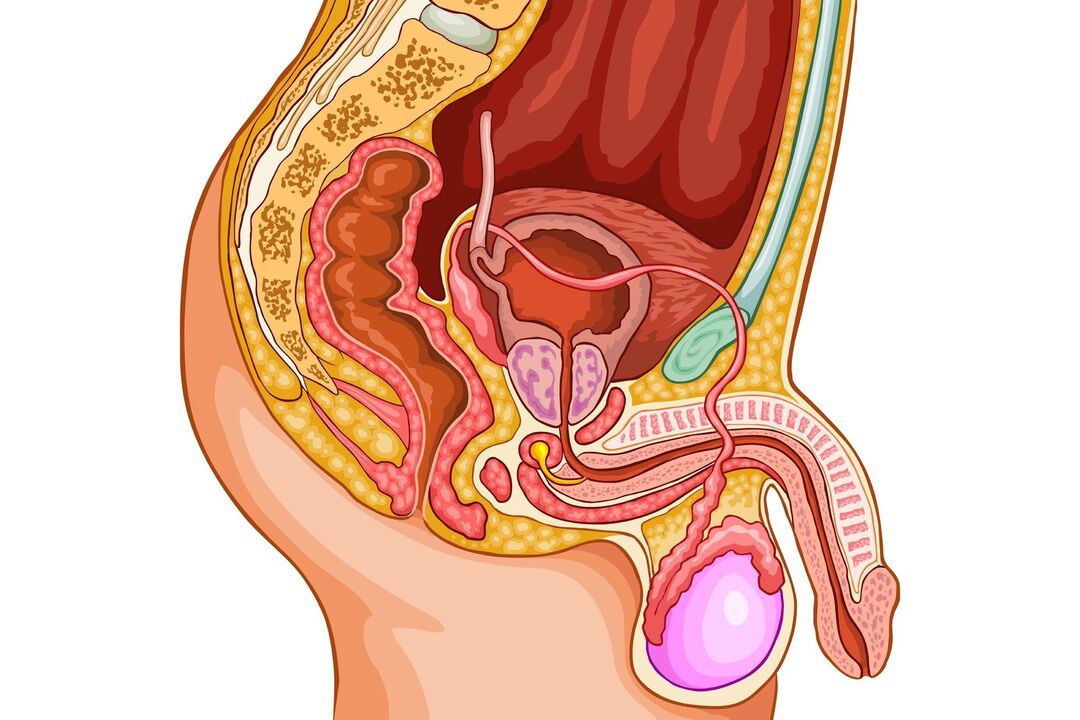
The inflammatory processes that occur in the prostate cause a lot of discomfort to men who suffer from this pathology. The development of the disease occurs against the background of prolonged sexual abstinence, the presence of sexually transmitted and genitourinary infections, weak immunity and various hormonal imbalances in the body. Additionally, prostatitis can be caused by pathogenic bacteria or viruses.
What is prostatitis and how to treat it?
The modern pharmaceutical market offers many highly effective drugs for the treatment of this pathology. When no infectious pathogens are found during the diagnosis of prostatitis, we speak of chronic inflammation of the prostate of a non-bacterial nature. The risk factors for non-infectious prostatitis are congestion in the pelvic area, which is characterized by an alteration of microcirculation in the venous system, an excess of secretion from the prostate and seminal vesicles, which causes alterations in blood flow. blood in the genitals. However, before starting therapy, it is always advisable to consult with a qualified specialist.
Characteristics of the inflammatory process of the prostate (prostatitis)
This disease affects 1/3 of all representatives of the stronger half of humanity. The pathology mainly affects men between 20 and 60 years old. The disease can develop in the presence of the following factors:

- Congenital (decreased hormonal levels, impaired blood flow in the prostate, pathological changes in the structure of the acini);
- acquired (previous genitourinary diseases, presence of foci of infection in the body, promiscuity or, conversely, prolonged abstinence from sexual relations, sedentary lifestyle, temporary decrease in body temperature).
Types of pathology and medications for treatment.
Prostate inflammation can manifest itself in the following ways:
Acute prostatitis of an infectious (bacterial) nature. It is characterized by the presence of specific symptoms and requires immediate contact with a specialist. Acute prostatitis develops as a result of exposure to pathogenic bacteria and microorganisms. According to statistics, this form of the disease occurs in 15% of men suffering from this pathology.
Acute prostatitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- shaking chills;
- increased body temperature;
- signs of general intoxication of the body;
- frequent urination, accompanied by pain and purulent discharge from the urethra;
- pain in the sulcus area, which radiates to the lumbar spine.
Chronic prostatitis of an infectious nature. It is a slow inflammatory process characterized by the absence of pronounced symptoms. This form of the disease can occur against the background of insufficiently treated or untreated acute prostatitis. Symptoms of prolonged inflammation of the prostate may be the following:
- Irritability;
- difficulty urinating, accompanied by a burning sensation;
- Persistent pain in the perineum, radiating to the pelvic organs and rectum.
Treatment of chronic prostatitis requires much more time than acute prostatitis, and the choice of drugs is determined by the individual characteristics of the body, the presence of complications and the type of drugs used previously.

In addition to antibiotics used to treat acute prostatitis, painkillers, immunomodulators, suppositories, therapeutic massages and physiotherapy are prescribed.
Prostatitis without infectious etiology. It is the most common type of disease, the origin of which has not yet been fully studied.
Asymptomatic prostatitis
Forms of medications for the treatment of prostatitis.
Medicines for the treatment of prostatitis are available in the form of tablets, injections, instillations, suppositories and microenemas. The tablets, which are usually antibiotics, have a wide spectrum of action and are usually prescribed in situations where the causative agent of the pathology has not yet been identified.
Often in the treatment of prostatitis, special suppositories are used, which are administered rectally. These drugs have an antibacterial effect and effectively relieve pain. The greatest therapeutic effect is provided by injectable solutions that have a stimulating effect on the vascular and protective systems of the body.
Among the various methods of prostate treatment, the rectal therapy method is the most effective.
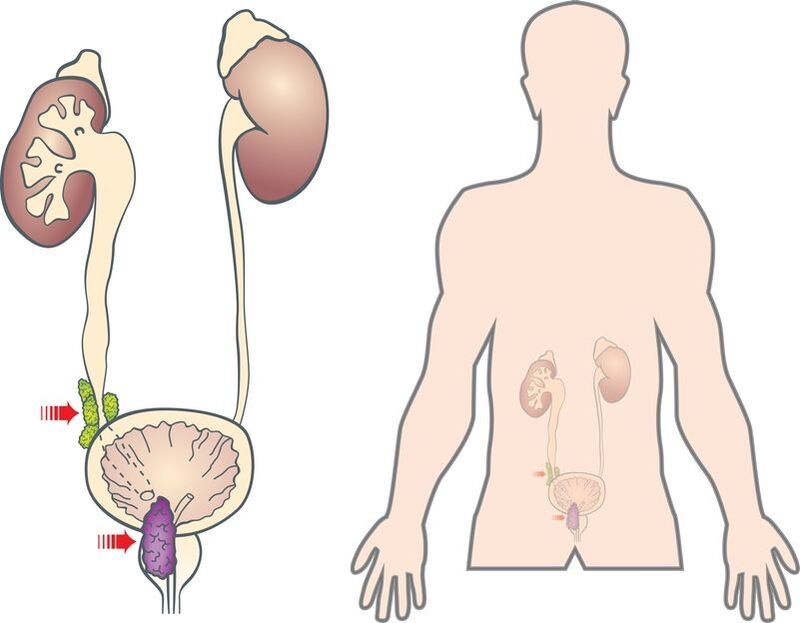
Treatment of prostatitis often involves a method such as instillation, in which a drug is injected directly into the patient's urethra. Before the procedure, the man must completely empty his bladder. No more than 5 ml of medicinal solution is administered at a time.
Additional means to the main treatment can be microenemas, which are prepared on the basis of herbal infusions and decoctions. The principle of this technique is to use a complex drug-temperature effect on the sources of inflammation. The procedure is carried out before going to bed, since after a microenema overstrain or hypothermia of the prostate is not allowed.
Medications for the treatment of prostatitis in men.
First of all, antibiotics are prescribed for this disease. But before starting antibacterial therapy, a bacterial culture study is carried out to determine the causative agent of the disease and, based on the results obtained, one or another type of drug is determined. The course of antibacterial therapy lasts an average of 1 month.
Treatment with antibiotics in tablets is carried out for bacterial inflammation of the prostate in acute and chronic forms. In case of complications, antibacterial agents are administered by injection. If the causative agent of the pathology cannot be identified, combined antibacterial therapy is used.
Medicines that have an analgesic effect significantly alleviate the course of the inflammatory process, but they must be used strictly as prescribed by the doctor. Uncontrolled use of these medications can cause unwanted side effects.
Among analgesics, the greatest effectiveness in the treatment of prostatitis has been demonstrated by a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug with an extended release form and a wide range of indications. The use of alpha blockers is due to the relaxing effect of these drugs on the neck and bladder muscles, which significantly reduces the intensity of pain accompanying the process of urination. But these medications can cause side effects such as headaches and hypotension. These medications are prescribed for chronic nonbacterial prostatitis.
Any pathology, including prostatitis, causes a weakening of the body's immune defenses, therefore, along with the main treatment, the doctor prescribes medications whose action is aimed at restoring and strengthening the immune system. These can be drugs from the group of immunomodulators, which includes interferons and other pharmacological agents.
Muscle relaxants are also widely used in the treatment of prostatitis, the action of which is aimed at reducing the tone of the muscles of the perineum, allowing the patient to get rid of pain and discomfort when urinating. The most effective muscle relaxants are considered to be centrally acting muscle relaxants and a remedy for pain and spasms of smooth muscles.
The use of hormone therapy is determined by the need to reduce testosterone levels, which cause an increase in the size of the prostate. As a result of such treatment, hormonal levels are normalized and the intensity of the inflammatory process decreases. In some cases, herbal remedies are used as additional therapy to eliminate pain, inflammation and swelling.
Preparations containing herbal components are often used in the treatment of chronic forms of prostatitis. Prostatitis of bacterial origin is treated with antiviral drugs: drugs that are used for the same indications, but differ in the mechanism of action and active ingredient.

As a complement, anti-inflammatory drugs from the non-steroidal group are used. The effect of these drugs is to eliminate the symptoms accompanying inflammation of the prostate (swelling and pain, increased body temperature).
Suppositories containing non-steroidal anti-inflammatory substances, for example, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, have shown high effectiveness in the treatment of prostatitis. This group also includes drugs that have powerful anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic effects.
Also, therapy for inflammation of the prostate involves the use of drugs whose action is aimed at improving blood flow to the prostate.
Popular medications for the treatment of prostatitis.
Medicine that helps in the treatment of diseases of the genitourinary system in men and women: a medicine based on plant components that prevents the growth of prostate glandular tissue. It helps eliminate inflammation and normalize metabolic processes, as well as improve blood supply to the prostate gland. In addition, the drug reduces the size of the prostate, eliminates difficulty urinating and improves the functioning of the genitourinary system, restores glandular functions, and also reduces swelling and inflammatory manifestations in the prostate gland.
The drug is prescribed for the complex therapy of complicated prostatitis. The course of treatment is up to 4 months. The medicine has no contraindications or side effects.
A bactericidal antibiotic from the group of semisynthetic penicillins, resistant to penicillinase, is a very effective antibiotic used to treat prostatitis. The drug is a semisynthetic antimicrobial drug that belongs to the class of β-lactam antibiotics and has bactericidal effects against streptococci, staphylococci and other gram-positive microorganisms.
A medicine intended for the treatment of various diseases of the genitourinary system in men is a suppository based on antibiotics with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects. The use of rectal suppositories improves sperm quality, helps restore muscle functions of the bladder, normalizes the urination process, and also reduces the risk of blood clots in the vessels of the prostate. Rectal suppositories are prescribed after prostate surgery or in the treatment of chronic prostatitis. The course of treatment lasts 10 days, with the administration of one suppository per day. Read the instructions carefully: the drug intended for the treatment of various diseases of the genitourinary system in men can cause a side effect, which is manifested by itching in the anus.
The medicine, which contains a natural ingredient - the extract of the fruits of the creeping palm tree, is available in capsules and belongs to decongestant and anti-inflammatory drugs. The drug has shown fairly high effectiveness in the complex treatment of inflammation of the prostate, therefore it is often prescribed to patients suffering from this pathology.
Popular antibiotics for the treatment of prostatitis.
Despite the fact that drugs for the treatment of prostatitis have practically no contraindications, you should not use them yourself. Dosage, selection of the drug and correction of the course of therapy are carried out only by a specialist, taking into account the intensity and duration of the inflammatory process.